A standard cost is one that a company expects at the outset of a year under a normal level of operational efficiency. Standard costs are used periodically as a basis for comparison with actual costs. The current category “Standard Costing and Variance Analysis” discusses the technique of standard costing and variance analysis, which is aimed at profit standard costing system improvement mainly by reducing materials, labor, and overhead costs. Activity-based costing (ABC) identifies overhead costs from each department and assigns them to specific cost objects, such as goods or services. These activities are also considered to be cost drivers, and they are the measures used as the basis for allocating overhead costs.
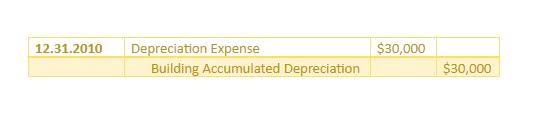
When cost accounting was developed in the 1890s, labor was the largest fraction of product cost and could be considered a variable cost. Workers often did not know how many hours they would work in a week when they reported on Monday morning because time-keeping systems (based in time book) were rudimentary. Cost accountants, therefore, concentrated on how efficiently managers used labor since it was their most important variable resource. Now, however, workers who come to work on Monday morning almost always work 40 hours or more; their cost is fixed rather than variable. However, today, many managers are still evaluated on their labor efficiencies, and many downsizing, rightsizing, and other labor reduction campaigns are based on them. The $100 credit to the Direct Materials Price Variance account indicates that the company is experiencing actual costs that are more favorable than the planned, standard costs.
Get Your Question Answered by a Financial Professional
The costs of these specific activities are only assigned to the goods or services that used the activity. This gives management a better idea of where exactly the time and money are being spent. Cost-accounting methods are typically not useful for figuring out tax liabilities, which means that cost accounting cannot provide a complete analysis of a company’s true costs. Cost accounting is a form of managerial accounting that aims to capture a company’s total cost of production by assessing the variable costs of each step of production as well as fixed costs, such as a lease expense. Nevertheless, standard costs are still found in the vast majority of manufacturing companies and many service companies, although their use is changing.
More important, it helps the management to set a proper price and compete in the market. While fixing standard costs, the fundamental principle to be observed is that the set standards are attainable so that these are taken as yardsticks for measuring the efficiency of actual performances. Basic standards provide the basis for comparing actual costs over time with a constant standard. The use of standard costs is also beneficial in setting realistic prices.
Standard cost accounting
Codes and symbols are assigned to different accounts to make the collection and analysis of costs more quick and convenient. Standard costs also assist the management team when making decisions about long-term pricing. The standard of efficient operation is decided based on previous experience, research findings, or experiments. The standard is generally defined as that which is attainable but only after substantial effort. Historical costing, which refers to the task of determining costs after they have been incurred, provides management with a record of what has happened.

A syllabus is one way an instructor can communicate expectations to students. Students can use the syllabus to plan their studying to maximize their grade and to coordinate the amount and timing of studying for each course. Knowing what is expected, and when it is expected, allows for better plans and performance. When your performance does not match your expectations, a variance arises—a difference between the standard and the actual performance. You want to know why you did not receive the grade you expected so you can make adjustments for the next assignment to earn a better grade. Standard costing provides management with accurate and timely data, enabling informed decision-making based on real-time cost information.
Definition of Standard Costing
It is a reflection of what is expected, under specific conditions, of plant and personnel. Standard cost offers a criterion against which actual costs incurred by the business can be measured and analyzed. Standard costs are predetermined costs that provide a basis for more effectively controlling costs. For managers within a company, exercising control through standards and standard costs is a creative program aimed at determining whether the organization’s resources are being used optimally.
CCR Responds to the FASB’s Proposed ASU on Disaggregation of Income Statement Expenses – FEI Daily
CCR Responds to the FASB’s Proposed ASU on Disaggregation of Income Statement Expenses.
Posted: Tue, 31 Oct 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
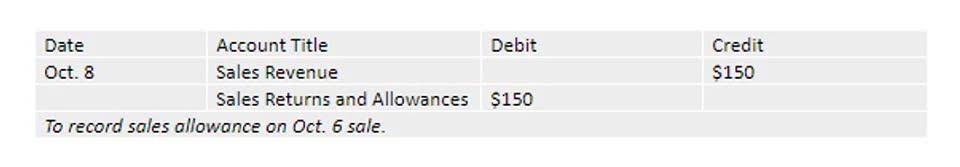
When used correctly, it can provide insights into where we need to make improvements. When misused, it can lead to faulty decision-making based on inaccurate information. As with any accounting method, standard cost accounting has pros and cons. The key is understanding these pros and cons and using the method to benefit your company. A favorable variance means that the actual incurred costs are less than the standard costs.
Standard Cost Accounting (or Standard Costing) is a form of cost accounting that uses predetermined costs for materials, labor, and overhead to estimate the costs of goods or services. Standard costing is typically used in manufacturing to determine the cost of products based on standard rates for materials, labor, and overhead. Companies use standard costing to set target costs for production and then compare actual production costs to the target costs. This comparison helps companies identify variances they need to address to improve their production processes. At the end of the accounting period, use the actual amounts and costs of direct material. Then utilize the actual amounts and pay rates of direct labor to compare it to the previously set standards.


